In Vitro Fertilization
What is IVF?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment has been used successfully for many years for couples who cannot have children with natural methods. In vitro fertilization, an assisted reproduction technique, offers couples who cannot have children due to infertility of undetermined cause, advanced age, infection and blockages in the tubes in women, low sperm count and low quality in men, and metabolic disorders such as obesity the opportunity to have children. In vitro fertilization treatment, which is the most preferred infertility treatment today, is an artificial fertilization technique applied by combining female and male reproductive cells under laboratory conditions and placing the fertilized egg in the mother’s uterus. This process is carried out by collecting the female reproductive cell, the egg, and the male reproductive cell, the sperm, under certain conditions. After the fertilization is completed in a healthy way, the egg is expected to start the division process and turn into a structure called embryo, and then the embryo is placed in the mother’s uterus and the pregnancy process begins as a result of successful attachment. After this stage, the pregnancy is no different from a natural pregnancy.
In IVF treatment, the egg cell taken from the mother and the sperm cells of the father are brought together in a laboratory environment outside the female reproductive system and an embryo is obtained when a sperm fertilizes the egg. As a result of implanting the embryo obtained in this way into the mother’s uterus, it becomes possible to create pregnancy in people who cannot conceive with normal methods.
If a woman who is under 35 years of age and who does not have any disease that may prevent her from conceiving cannot conceive despite having unprotected and regular sexual intercourse for 1 year, she should definitely be examined and if necessary, she should apply for treatment. Women who are over 35 years of age or who have had any problems affecting conception before should try for 6 months. If pregnancy has not occurred at the end of this period, the necessary treatment procedure should be started as soon as possible in order not to progress further and lose time.
IVF is a common and increasingly successful treatment method. These treatments are applied due to women’s tubal problems, ovulation problems and male infertility, and many applications are on the agenda to increase the success of treatment.
In vitro fertilization is generally recommended to be performed 3 times. There is a possibility of pregnancy in the trials after this number, but the chances are very low.
IVF treatment can be applied in women until the age of 45. However, it should be taken into account that the chance of getting pregnant decreases significantly in women over the age of 40. For this reason, the success rate of IVF in older women is lower than in younger women and the number of attempts may need to be increased.
Factors such as the age of the expectant mother and embryo quality are of great importance in the success of IVF. Therefore, the chance of success varies according to these factors. While the success rate of IVF in women under 30 years of age is 55-60%, this rate decreases to 15-20% in women over 40 years of age.
10 Questions Wondered in IVF Treatment
With the medical technologies that have developed in recent years, the success rate in IVF treatments has increased, and many couples who were considered impossible to have a child have been able to have a healthy child thanks to this treatment. We have compiled 10 questions about IVF treatment for you,
How is the egg collected? Is it a painful procedure?
Under vaginal ultrasound guidance, a special needle is inserted into the ovaries and the fluid-filled structure called the follicle, where the egg is located, is drained. The fluid removed with the needle is transferred into a tube. The fluid in the tube contains eggs with very small cells that can be seen under a microscope. Egg retrieval is not a painful procedure, but it is better done under light or general anesthesia so that patients are not uncomfortable.
How are the embryos implanted in the uterus after fertilization?
Embryo transfer into the uterus is a very simple and short procedure. First, a thin plastic catheter is inserted into the cervix by the specialist. The embryo is transferred to the mother’s uterus through this catheter. Due to the egg-enhancing injections administered before the procedure, more embryos than the required number of embryos may be obtained. In this case, the quality embryos that are not transferred can be frozen and stored.
Should I rest after embryo transfer?
It is recommended that expectant mothers rest for the first 45 minutes after embryo transfer. After 45 minutes, the expectant mother who is allowed to leave the hospital does not need to rest. There is no harm in continuing her daily activities and work life. After the transfer, the expectant mother can return to all normal life activities except sports activities such as heavy exercises, brisk walks and sexual activities.
When can the person return to normal activities after the transfer? Is the sexual life affected?
After the transfer, the expectant mother can resume all normal life activities except for sports activities such as heavy exercises, brisk walks and sexual activities. Especially in the first week after the transfer, sexual intercourse is not recommended for expectant mothers. The reason for this is that the ovaries enlarge slightly due to the egg development treatments and procedures applied. However, the necessity of this practice has not yet been scientifically proven.
What are the pregnancy outcomes from frozen embryos?
The rate of pregnancy from frozen embryos varies depending on the quality of the IVF center’s laboratory. It is of great importance that the embryos obtained by specialists are stored under appropriate conditions.
What is done if the sperm count is too low or there are no sperm in the sperm test?
If the sperm count is lower than the desired ratio, in vitro fertilization treatment with microinjection is performed. With this method, it is possible to achieve successful fertilization even with a low sperm count. If there is no sperm in the semen, a surgical procedure is performed to search for sperm in the testicles.
Should a special diet be followed during IVF treatment?
Although there are not enough studies on this subject, studies show that IVF rates increase in patients who consume diets based on Mediterranean cuisine (vegetable oils, fish, legumes, vegetables) during the period when pregnancy is considered (preconceptional period).
Is there a higher risk of miscarriage after IVF?
The risk of miscarriage in IVF pregnancies is slightly higher than in natural pregnancies. However, this result is not due to the IVF treatment. The increased risk of miscarriage is attributed to the reason that prevented the person from conceiving.
What is blastocyst transfer?
It is a method that aims to increase the chances of conception for patients who have tried in vitro fertilization. Blastocyst transfer is the development of the embryo on the 5th day of the embryo, which is formed by bringing together egg and sperm cells that have failed to get results many times and leaving them to fertilize. The quality embryo, which does not have any genetic problems and no structural defects are detected, is examined in the laboratory environment and transferred to the uterus of the expectant mother. This method is highly successful.
Is sexual abstinence necessary during IVF treatment?
Sexual abstinence is only required for 3 to 5 days before the egg retrieval procedure, as it is aimed to ensure that the sperm count and motility are at the appropriate level. It is recommended that you consult your physician about sexual abstinence after the transfer.
*Page content is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Process
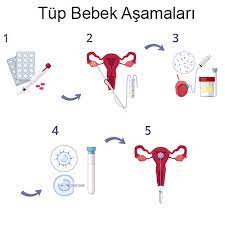
Ovarian stimulation treatment is performed with injections containing the hormone FSH, which can be administered under the skin. Rarely, it may cause redness and sensitivity of the skin. These injections are: Gonal F, Puregon, Fostimon, Menogon, Menopur, Meriofert. Although their production technologies are different, they have not been shown to be superior to each other.
Stimulation treatment lasts an average of 10 days. During this period, the number and diameter of the egg sacs (follicles) are measured 3-4 times by vaginal ultrasound and the progress is monitored. Generally, on the day when the largest follicles reach 18 mm in diameter, 2 cracking needles (Gonapeptyl 0.1 mg) are administered under the skin one after the other. Approximately 36 hours after this injection, egg collection is performed.
It is performed under mask anesthesia. In the procedure, the fluid from each follicle (egg sac) is aspirated with a special syringe needle through the vagina under ultrasound guidance. Eggs are extracted from this fluid, which is sent to the laboratory. The procedure takes 5-10 minutes in total, and if necessary, hysteroscopy and laparoscopy can be performed together. A sperm sample is taken from the man while the patient is resting in the room. For this procedure, the duration of sexual abstinence is kept between 1-2 days. After the anesthesia effect wears off, the patient can leave the center on foot.
Eggs fertilized with sperm on the day of egg retrieval are kept in special culture media for 4-6 days and their daily development is observed. Embryos, which develop by actively dividing every day, have 4 cells on day 2 and 8 cells on day 3, while the cells that multiply on day 4 begin to transform into a ball of cells by fusion. On the fifth and sixth days, they take on a different appearance called a blastocyst with fluid accumulation in the middle of this ball of cells. On average, one out of every 3 fertilized eggs develops this feature.
Embryos are frozen at -196 degrees in tanks containing liquid nitrogen in tubes with special protective liquid and stored until the day of transfer. The embryo to be used in the first attempt is frozen and implanted on average 30 days later. All remaining embryos can be safely stored for up to 5 years for backup purposes. At the end of these 5 years, the period may be extended.
On the day of the planned transfer, the embryo to be transferred is thawed after obtaining the patient's consent. An appointment is usually made for 6-7 hours after thawing. A small amount of urine is required. While the patient is in the operating room in the examination position, the embryo in the catheter brought from the laboratory is placed into the uterus. Since the procedure is painless, anesthesia is not required. Bed rest is not recommended afterwards.
*Page content is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
After treatment
What should be considered after the transfer?
The biggest misconception is that the implanted embryo can be aborted. Scientifically, this is not the case. On the contrary, we do not recommend bed rest because it leads to decreased blood circulation and increased stress. Immediately afterwards, it is permitted to go to the toilet, walk, climb up and down stairs, do daily chores at home, travel by car or plane. Bathing, sexual intercourse, sea and pool are not prohibited. There is no special diet and nutrition. In case of constipation, syrup-like medications that are not absorbed by the intestine should be used.
IVF Pregnancy
An IVF pregnancy is no different from a natural pregnancy. What makes it different is that it is achieved with great longing and difficulty. The disadvantages of IVF pregnancy, which may include pregnancy loss, are listed below.

The blood pregnancy test is hCG. It is a blood test taken 9 days after the transfer. The value, which is around 100 IU at first, should increase at least 2 times every other day. The risk of loss is high in patients whose hCG value starts below 50 or does not double. This condition is called chemical pregnancy. This condition, which is 5% common, disappears with menstrual bleeding without intervention.
This can happen even if the pregnancy test shows a high hCG level and a doubling every 2 days. About 10 days after the first blood test, a vaginal ultrasound will show the gestational sac. However, no heartbeat can be detected in the following weeks. It is responsible for about 5% of pregnancy losses. It is believed to be caused by genetic or structural defects in the embryo.
It refers to the loss of heartbeats after heartbeats have been monitored in previous checks. It is believed to be caused by genetic or structural defects in the embryo, as well as structural problems in the uterus, such as a curtain that reduces nutrition or clotting disorders.
This often harmless condition causes fear because it is perceived as a threat of miscarriage. In this condition, which is caused by the cracking of small vessels in the placenta, progesterone-containing drugs are often used in combination with bed rest. It is rare for bleeding to cause pregnancy loss.
Negativities affecting the pregnancy process such as anemia, diabetes, hypertension, thyroid diseases are investigated in average monthly controls. If there is no familial risk, a 50 g sugar loading test is performed in the 26th week.
The double test at 12-13 weeks and the quadruple test at 16-17 weeks are used to screen for Down syndrome. These tests are screening tests and have a sensitivity of 70%. The "fetal DNA test in maternal blood" or NIFT test is 99% diagnostic. We do not recommend the NIFT test because of the risk of pregnancy loss during amniocentesis. In addition, since the baby's organs can be observed most clearly on ultrasound at the 20th week, a "detailed anomaly screening" should be performed by a perinatologist or radiologist specialized in this field.
Especially in the 20th week, the cervix should be measured by vaginal ultrasound to prove that there is no insufficiency. Since the risk of preterm birth increases 4 times in twin pregnancies, we recommend this control monthly. When this length, which should normally be 4 cm, decreases to 2 cm, cerclage suture is recommended to strengthen that area during pregnancy. In addition, progesterone treatment is also effective in patients who have already given birth prematurely until the risk disappears.
It is not an obstacle to normal birth. Caesarean section is more preferred because it is difficult and laborious to achieve.
*Page content is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Necessary Tests
Women - Investigations
- Blood Group (ABO)
- Determination
- Creatinine
- Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
- Fasting Blood Glucose
- Hgb A1C
- Prolactin (PRL)
- Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Hepatitis B s Antigen (HBsAg)
- Rubella Antibody lgG
- Toxoplasma Antibody lgG
- Hepatitis C Antibody (anti-HCV)
- HIV Antibody (1-2)
- VDRL
- Complete Urine
- Hemogram
- Anti Hbs ag
- Covid -19
Male - Investigations
- Hepatitis B s Antigen (HBsAg)
- Hepatitis C Antibody (anti-HCV)
- HIV Antibody (1-2)
- VDRL
- Blood Type
- Semen Analysis
- Covid – 19
*Page content is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Services offered
- In vitro fertilization
- Genetic disease analysis
- Tesa
- Micro tese
- Embryo freezing
- Sperm freezing
- Egg freezing
- Hotel accommodation
- Transportation
- Airfare

